Hypertensive heart disease is a long-term condition that develops in people with high blood pressure over time. It is a group of medical problems that can occur when you do not control your high blood pressure, such as heart failure and conduction arrhythmias (hypertension).
Chronically high blood pressure (greater than 120/80 mmHg) causes hypertensive heart disease. People who continue to have high blood pressure as they age are more likely to develop heart disease. Heart failure is more common in people over the age of 65.
Best Heart specialists and Cardiologists in Delhi
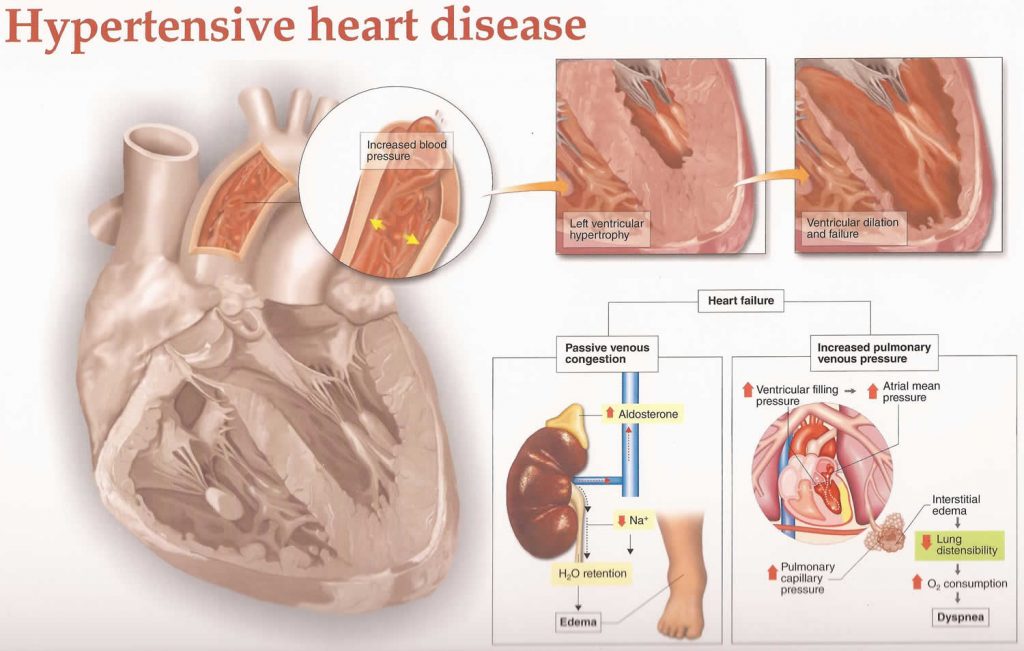
Chronic high blood pressure strains your heart and makes it work harder to pump blood. The muscle in your heart can become thick and weak, potentially leading to heart failure. High blood pressure can cause the walls of your blood vessels to thicken, which becomes more dangerous when cholesterol accumulates inside the blood vessels.
Men are twice as likely as women to develop heart failure if they have high blood pressure. People who manage their high blood pressure, on the other hand, can significantly reduce their risk of heart failure.
Heart specialist doctor in Delhi
People with hypertensive heart disease and heart failure are more likely to develop:
Heart failure due to under compensation.
Acute coronary syndrome (ACS).
Unexpected cardiac death.
What types of hypertensive heart disease exist?
High blood pressure makes your heart work harder to push blood through your blood vessels. When plaque builds up in your blood vessels or a portion of your heart muscle enlarges due to high blood pressure, you can develop the following issues:
Coronary artery disease (CAD)
Hypertrophy of the left ventricle (enlarged heart).
What are the complications of hypertensive heart disease?
Hypertensive heart disease complications include:
• Failure of the heart.
• Arrhythmia.
• Stroke.
• Ischemia of the heart.
• Unexpected cardiac death.
People with high blood pressure are at risk for:
• Atrioventricular fibrillation.
• Heart failure with congestive edoema.
• Coronary artery disease (CAD)
• Atherosclerosis.
• Disease of the retina.
• Atherosclerosis of the peripheral arteries.
• Kidney disease that is chronic.
• Aneurysm of the aorta.
• Cerebral vascular disease (CVD).
How widespread is hypertensive heart disease?
One in every three adults in the United States has high blood pressure, but only half of those with the diagnosis have it under control. The leading cause of illness and death due to high blood pressure is hypertensive cardiovascular disease.
Who is susceptible to hypertensive heart disease?
You have hypertensive heart disease if you:
• I suffer from high blood pressure.
• Don’t work out.
• I’m diabetic.
• Have a high cholesterol level.
• Are over the age of 45.
• Are you overweight?
• Tobacco use or smoking is prohibited.
• Consume a lot of salt.
• Consume alcoholic beverages.
What factors contribute to hypertensive heart disease?
Hypertensive heart disease is caused by uncontrolled high blood pressure for many years.
What are the signs and symptoms of hypertension?
Many people are unaware they have high blood pressure because there are no symptoms. Hypertensive cardiovascular disease symptoms frequently appear after your heart has already been damaged.
Hypertensive heart disease symptoms include:
• Chest ache
• Breathing difficulty.
• Palpitations.
• Dizziness.
• Fainting.
• Stroke.
• Unexpected cardiac death.
What is the treatment for hypertensive heart disease?
Your provider will address any medical issues you may be experiencing, such as:
• Blood pressure is high.
• Diabetes.
• Obesity.
• Disease of the lungs.
• Apnea while sleeping.
• Kidney disease that is chronic.
• High cholesterol levels.
Your provider may request that you modify your lifestyle in the following ways:
• Quit smoking and stop using tobacco products.
• Reduce your alcohol consumption.
• Stop using drugs for fun.
• Increase your physical activity.
• Consume less sodium.
• Reduce your weight.